Author : Nuzzu.S
Date : August 30, 2024
Introduction
Cryptocurrency has revolutionized the financial landscape, and India is very much part of this transformation. With the rising popularity of digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others, more and more Indians are diving into the crypto market. But as the excitement around cryptocurrency grows, so does the complexity of understanding its tax implications. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just getting started, it’s crucial to understand how cryptocurrencies are taxed in India to avoid any legal pitfalls and optimize your tax planning.
Regulatory Landscape of Cryptocurrency in India
Cryptocurrency in India has had a tumultuous journey. Initially, the Reserve Bank of India[1] (RBI) placed a ban on banks facilitating crypto transactions, creating an air of uncertainty. However, in 2020, the Supreme Court lifted this ban, allowing the crypto market to flourish once more. The Indian government has since been exploring ways to regulate cryptocurrency, with various committees and stakeholders weighing in on the issue.

Classification of Cryptocurrency for Tax Purposes
One of the biggest questions around cryptocurrency in India is its classification for tax purposes. Is it a currency, an asset, or something else entirely? This question’s answer is crucial because it determines how to tax cryptocurrency transactions.
Taxable Events in Cryptocurrency Transactions
Not every cryptocurrency transaction triggers a tax liability. However, certain events do constitute taxable events under Indian tax laws. These include:
- Buying and Selling of Cryptocurrencies: If you sell your cryptocurrency for a profit, you are liable to pay capital gains tax on the profit earned.
- Receiving Cryptocurrency as Payment: If you receive cryptocurrency as payment for goods or services, it is treated as income and taxed accordingly.
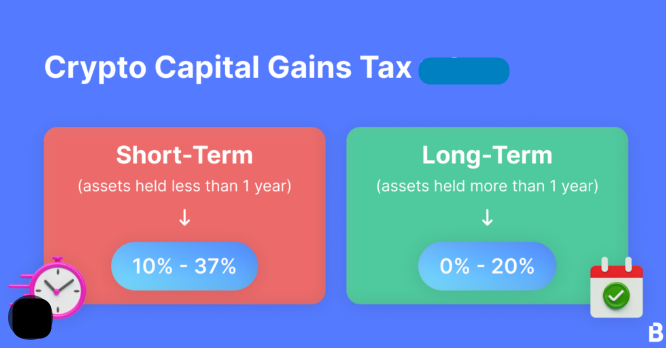
Capital Gains Tax on Cryptocurrency
When it comes to capital gains tax on cryptocurrency, the holding period plays a crucial role.
- Short-term vs. Long-term Capital Gains: If you hold your cryptocurrency for less than 36 months before selling, it is considered a short-term capital gain, taxed at your applicable income tax slab rate. If held for more than 36 months, it is treated as a long-term capital gain, typically taxed at 20% with indexation benefits.
- Calculation of Capital Gains: The capital gain is calculated as the difference between the selling price and the purchase price (cost of acquisition) of the cryptocurrency. Indexation benefits can reduce the taxable amount for long-term gains.
Income Tax on Cryptocurrency Earnings
- How Cryptocurrency Earnings are Taxed as Income: Earnings such as airdrops, staking rewards, and referral bonuses are treated as income and taxed at the applicable income tax rate.
- Different Income Sources in Cryptocurrency: These include mining, staking, airdrops, and receiving cryptocurrency as a gift or payment for services. Income tax applies to each of these, and you must maintain proper records to report them accurately.
GST Implications on Cryptocurrency Transactions
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is another important consideration for cryptocurrency transactions.
- Is GST applicable to cryptocurrency transactions? The applicability of GST on cryptocurrency transactions is a gray area.
- GST on Buying and Selling Cryptocurrencies: If considered as goods, the buying and selling of cryptocurrencies could attract GST. However, this is still a developing area, and investors should stay updated on any new regulations.

International Transactions and Cryptocurrency
With cryptocurrencies being a global phenomenon, international transactions are common.
- Taxation on International Crypto Transfers: International transfers of cryptocurrency may attract taxes based on the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAA) between India and the other country involved.
- Reporting Foreign Crypto Holdings: Indian residents holding cryptocurrency in foreign exchanges must report these holdings as part of their foreign assets in the Income Tax Return (ITR). Failure to do so can lead to penalties.
Tax Compliance and Reporting Requirements
Compliance is key when it comes to cryptocurrency taxation.
- How to Report Cryptocurrency Transactions in ITR: All cryptocurrency transactions, whether they result in gains or losses, must be reported in your ITR. This includes buying, selling, receiving, and mining cryptocurrencies.
- Penalties for Non-compliance: Non-compliance with crypto tax regulations can result in hefty penalties and even legal action. It is crucial to maintain accurate records and report all transactions correctly[2].
Legal Challenges and Gray Areas
The cryptocurrency tax landscape in India is still evolving, leading to several legal challenges and gray areas.
- Lack of Clear Guidelines from Authorities: The lack of comprehensive guidelines from tax authorities creates uncertainty for crypto investors, especially regarding classification and GST implications.
- Potential Legal Challenges for Crypto Users: As regulations develop, there may be retroactive taxation or new rules that could impact past transactions. Staying informed and consulting with a tax professional is advisable.
Recent Developments in Cryptocurrency Taxation
The Indian government is gradually addressing cryptocurrency taxation.
- Changes Introduced in Recent Union Budgets: Recent budgets have introduced provisions[3] for taxing virtual digital assets, signaling the government’s intent to bring cryptocurrency under the tax net.
- Impact of Recent Court Rulings on Crypto Taxation: Court rulings, particularly the Supreme Court’s stance on the RBI’s crypto ban, have played a significant role in shaping the regulatory and taxation landscape.

Tax Planning Strategies for Cryptocurrency Investors
Effective tax planning can help minimize liabilities.
- How to Minimize Tax Liability Legally: Strategies such as holding assets for the long term, utilizing indexation benefits, and leveraging tax-efficient investment[4] vehicles can reduce your tax burden.
- Importance of Professional Tax Advice: Given the complexity of crypto taxation, seeking advice from a professional with expertise in this area is highly recommended.
The Future of Cryptocurrency Taxation in India
The future of cryptocurrency taxation in India is still uncertain, but trends are emerging.
- Potential Future Regulations: The government may introduce clearer regulations and possibly new taxes specific to cryptocurrency in the future.
- Impact of Global Crypto Taxation Trends on India: As global trends evolve, India is likely to align its taxation policies with international standards, especially regarding cross-border transactions[5].
Conclusion
Navigating the tax implications of cryptocurrency in India can be complex, but it’s crucial for anyone involved in the crypto space. By understanding how cryptocurrencies are classified and taxed, keeping accurate records, and staying informed about regulatory changes, you can ensure compliance and optimize your tax planning.
FAQs
How is cryptocurrency taxed in India?
Cryptocurrency in India is taxed based on the type of activity, such as trading, mining, or staking. Earnings are generally subject to income tax, capital gains tax, and GST, depending on the nature of the transaction.
Do I need to pay taxes on cryptocurrency mining?
Yes, earnings from cryptocurrency mining are considered income from other sources and are subject to income tax. Miners can deduct expenses related to mining activities, such as electricity and hardware costs.
What happens if I don’t report my cryptocurrency earnings?
Failing to report cryptocurrency earnings can result in severe penalties, including fines and legal action. The Income Tax Department has increased its scrutiny of cryptocurrency transactions, making compliance essential.
How can I reduce my tax liability on cryptocurrency?
To reduce your tax liability on cryptocurrency, consider long-term investments to benefit from lower capital gains tax rates. Additionally, you can deduct expenses related to mining and trading activities.
Is there any tax exemption for small cryptocurrency investors?
Currently, there are no specific tax exemptions for small cryptocurrency investors in India. All cryptocurrency earnings are subject to tax, regardless of the amount.





