AUTHOR-ELIZA FERNZ
DATE-31/8/2024
INTRODUCTION
In recent years, India has made significant strides in technological advancements, particularly in the financial sector. The launch of India’s digital currency platform marks a pivotal moment in the country’s economic evolution, promising to transform the way transactions are conducted(1) and managed. In this blog post, we’ll explore what the Digital Currency Platform is, its potential benefits, and the impact it could have on India’s financial landscape.

What is India’s Digital Currency Platform?
India’s Digital Currency Platform, officially known as the Digital Rupee (e₹), represents a state-backed digital currency initiative that the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) spearheads. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which operate on decentralized networks(2), the RBI controls and issues the digital rupee as a central bank digital currency (CBDC).
The primary goal of the digital rupee is to provide a secure, efficient, and accessible means of payment and transaction processing. By leveraging digital technology, the RBI aims to enhance financial inclusion(3), reduce transaction costs, and bolster the efficiency of the financial system.
Key Features of the Digital Rupee
1. Centralized Control
Unlike decentralized cryptocurrencies, the digital rupee is managed and regulated by the RBI. This centralized control ensures stability(4), trust, and compliance with regulatory standards, which are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the financial system.
2. Enhanced Security
The Digital Rupee is designed with robust security features to protect users against fraud(5) and cyber threats. Advanced encryption techniques and secure transaction protocols ensure that digital transactions are safe and reliable.
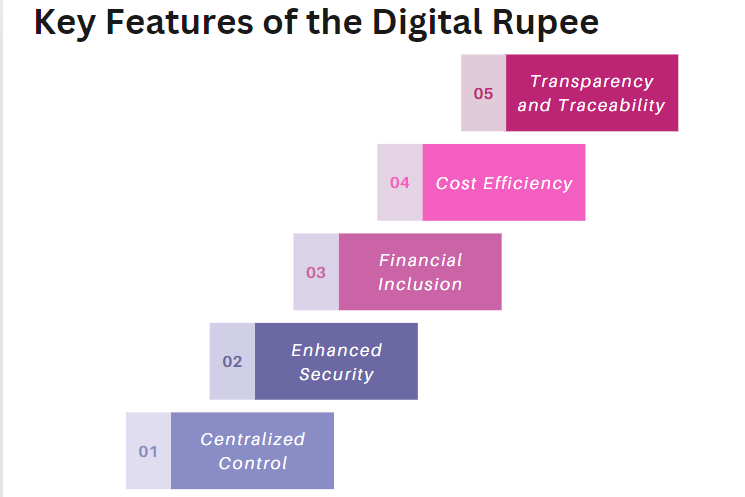
3. Financial Inclusion
One of the core objectives of the Digital Rupee is to promote financial inclusion. By providing a digital currency accessible through various platforms and devices, the RBI aims to bring banking services to underserved and remote areas of India.
4. Cost Efficiency
Digital transactions generally involve lower costs compared to traditional payment methods. By reducing the need for physical infrastructure and streamlining transaction processes, the digital rupee can help lower transaction fees and operational costs for businesses and consumers alike.
5. Transparency and Traceability
The digital rupee offers enhanced transparency and traceability in transactions. Every transaction is recorded and can be tracked, which helps reduce financial crime and improve regulatory oversight.
Benefits of the Digital Rupee
1. Streamlined Transactions
With the Digital Rupee, transactions can be processed instantly, eliminating the delays often associated with traditional banking systems. This efficiency is particularly beneficial for businesses and individuals engaged in frequent transactions.
2. Reduced Cash Dependency
The introduction of digital currency reduces the reliance on physical cash, which can be prone to issues such as theft and counterfeiting. A digital currency system minimizes these risks and supports a more secure financial environment.
3. Support for Innovation
The digital rupee can serve as a catalyst for innovation in the financial technology sector. It opens up new opportunities for developing digital payment solutions, financial services, and applications that can further enhance the user experience.

4. Economic Growth
By fostering a more efficient and inclusive financial system, the digital rupee has the potential to stimulate economic growth. It can support entrepreneurship, boost consumer spending, and improve overall economic stability.
Potential Challenges
While the digital rupee offers numerous advantages, it also presents certain challenges. These include:
- Cybersecurity Risks: Despite advanced security measures, digital currencies are still vulnerable to cyberattacks. Ensuring the safety of digital transactions is crucial.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Widespread adoption of the digital rupee requires significant investments in digital infrastructure and technology.
- Public Acceptance: Gaining public trust and encouraging widespread use of the digital rupee will be essential for its success.
Conclusion
India’s Digital Currency Platform represents a significant leap forward in the country’s financial evolution. By offering a secure, efficient, and inclusive means of transaction, the digital rupee has the potential to reshape the financial landscape and drive economic growth. As the platform continues to develop, it will be important to address the associated challenges and ensure that the benefits are maximized for all stakeholders.
As we look towards the future, the digital rupee stands as a testament to India’s commitment to innovation and progress in the digital age. Whether you’re a business owner, consumer, or financial professional, keeping an eye on the developments of India’s digital currency platform will be essential in navigating the changing financial landscape.
FAQ’S
1. What is India’s Digital Currency Platform?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issues and regulates India’s digital currency platform, known as the digital rupee (e₹). As a Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), the digital rupee functions to provide a secure and efficient means of digital transactions.
2. How does the digital rupee differ from cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin?
Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which operate on decentralized networks and lack central control, the digital rupee is a central bank digital currency (CBDC) that is centrally managed and regulated by the RBI. This central control ensures stability, compliance, and security in the financial system.
3. What are the primary benefits of the digital rupee?
The digital rupee offers several benefits, including:
- Enhanced Transaction Efficiency: Faster and more efficient transactions compared to traditional payment methods.
- Financial inclusion: increased access to financial services for underserved and remote areas.
- Cost Reduction: Lower transaction fees and operational costs.
- Increased Security: Advanced security measures to protect against fraud and cyber threats.




