Author : Nuzzu .S.
Date : 22 August 2024
Introduction
Currency plays a pivotal role in any economy, and India is no exception. For decades, traditional currency, governed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), has been the backbone of financial transactions[1]. However, with the advent of technology, a new form of currency—cryptocurrency[2]— has emerged, challenging the conventional norms of money. As India stands on the brink of a digital revolution, the comparison between cryptocurrency and traditional currency[3] becomes increasingly significant. In this article, we will explore the key differences, advantages, challenges, and future prospects of both forms of currency in India.
What is traditional currency?
Traditional currency, also known as fiat money[4], is the standard medium of exchange issued by a country’s government. In India, the Indian Rupee (INR) is the official currency[5], and it has a rich history dating back to ancient times. The evolution of the rupee has seen it transition from coins made of precious metals to the paper notes and digital forms we use today.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central authority responsible for regulating and issuing traditional currency in India. It ensures the stability and integrity of the currency by managing its supply and controlling inflation through various monetary policies.
What is cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency[1] that uses cryptographic techniques to ensure security. Unlike traditional currency, it is decentralized and operates on blockchain technology, which is a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers.
Globally, cryptocurrencies[2] like Bitcoin[3], Ethereum, and Ripple have gained significant popularity, and India is no exception. In India, Bitcoin is the most recognized cryptocurrency, followed by others like Ethereum, Binance Coin, and Dogecoin.
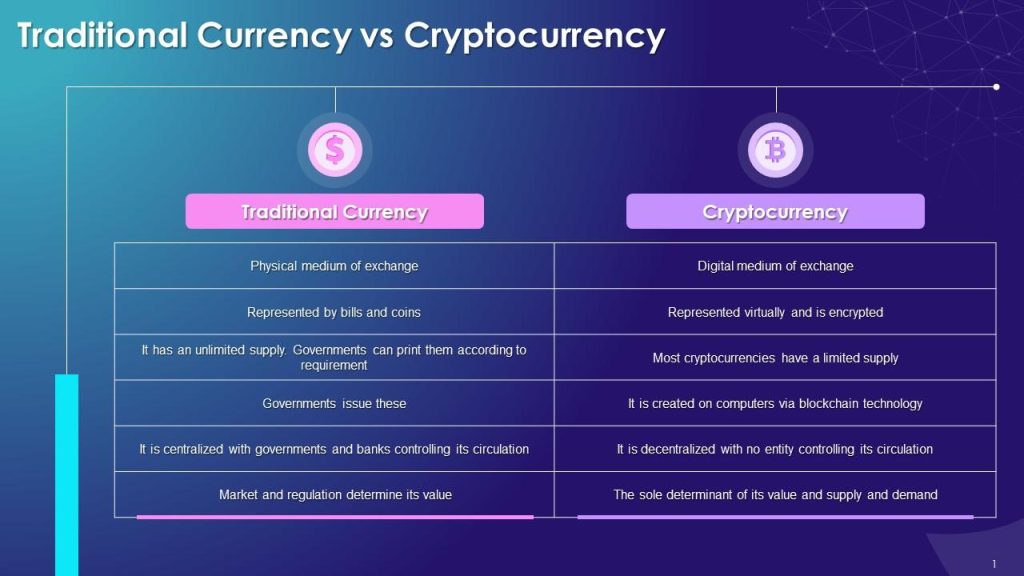
Key Differences Between Cryptocurrency and Traditional Currency
Tangibility and Form
Traditional currency is tangible; it exists in the form of coins[4], notes, and bank deposits. Cryptocurrency, on the other hand, is entirely digital, with no physical presence. It exists solely as data on the blockchain.
Regulation and Governance
Traditional currency is heavily regulated by central banks[5] and governments, ensuring stability and trust. Cryptocurrency operates in a decentralized manner without a central authority, leading to a lack of formal regulation, which can be both a strength and a weakness.
Transparency and Anonymity
Cryptocurrency transactions are transparent and recorded on a public ledger, but offer a high degree of anonymity to users. Traditional currency transactions, especially digital ones, are monitored by financial institutions, providing less anonymity but more security against illegal activities.
Stability and Volatility
Traditional currency is relatively stable, with its value controlled by the central bank. Cryptocurrency is known for its extreme volatility, with values fluctuating based on market demand, investor sentiment, and global events.
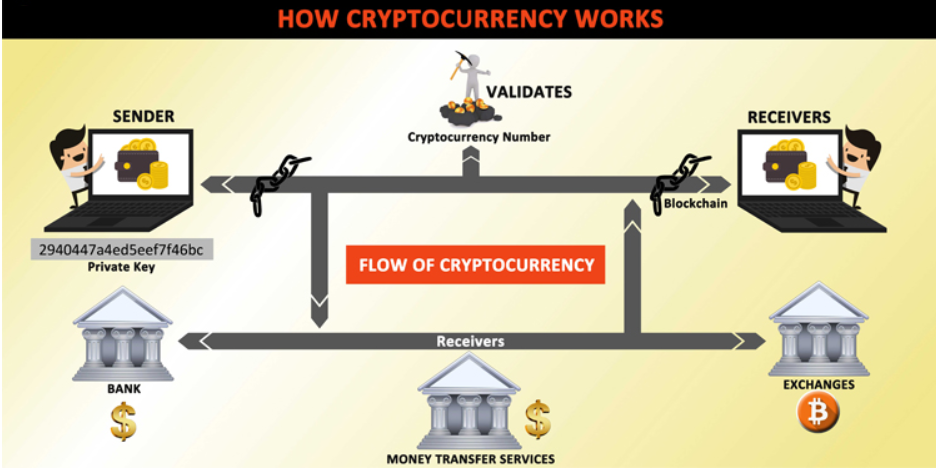
How Cryptocurrency Works
Cryptocurrency operates on blockchain technology, a decentralized system where transactions are recorded on a public ledger. This ledger is maintained by a network of computers, known as nodes, that validate and record each transaction.
To acquire cryptocurrency, one can either purchase it through an exchange or mine it. Mining involves solving complex mathematical problems to add a new block to the blockchain, which in turn generates new coins as a reward.
Cryptocurrency is stored in digital wallets, which can be online, offline, or hardware-based. Transactions are conducted directly between users, without the need for intermediaries like banks.
How Traditional Currency Works
Traditional currency operates within a centralized banking system, where banks and financial institutions act as intermediaries in transactions. Whether you’re using cash, a credit card, or an online banking service, these transactions are processed through a network of banks and clearinghouses.
In India, the RBI plays a crucial role in the functioning of traditional currency, regulating its supply, controlling inflation, and ensuring financial stability. Traditional currency can be used in both physical and digital forms, making it versatile and widely accepted.
Advantages of Cryptocurrency
Decentralization and Autonomy
One of the main advantages of cryptocurrency is its decentralized nature, which provides users with autonomy over their funds without relying on a central authority. This independence is appealing to those who value privacy and control over their financial assets.
Lower Transaction Costs
Cryptocurrency transactions typically have lower fees compared to traditional banking systems, especially for cross-border payments. This makes it appealing for cross-border transactions.
Speed and Efficiency
Cryptocurrency transactions are fast, often completed within minutes, regardless of the amount or destination. This efficiency contrasts with the delays that can occur with traditional banking, particularly in international transfers.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Cryptocurrency offers financial inclusion to people who are unbanked or underbanked, providing them with access to financial services without the need for a traditional bank account.
Advantages of Traditional Currency
Stability and Trust
Traditional currency is backed by the government and regulated by central banks, which ensures its stability and trustworthiness. This reliability is essential for the smooth functioning of an economy.
Wide Acceptance and Use
Traditional currency is universally accepted, making it easier to use in everyday transactions. It is also deeply integrated into the global financial system, which ensures its widespread acceptance.
Regulatory Protection
Users of traditional currency benefit from regulatory protection, including fraud prevention, consumer rights, and dispute resolution mechanisms, which provide a layer of security not yet available in the cryptocurrency world.
Physical Presence and Tangibility
The physical nature of traditional currency offers a sense of security and tangibility, which many people still prefer over the abstract concept of digital money.
Challenges of Cryptocurrency in India
Regulatory Uncertainty
One of the biggest challenges for cryptocurrency in India is the lack of clear regulations. The legal status of cryptocurrencies has been a topic of debate, with the government expressing concerns over their potential misuse.
Security Concerns
Despite its robust technology, cryptocurrency is not immune to hacking, scams, and other security issues. The lack of regulation also means there is no recourse for users who fall victim to such attacks.
Volatility in Value
Cryptocurrency is highly volatile, with prices swinging wildly in short periods. This instability can be a significant deterrent for those looking for a stable store of value.
Limited Acceptance
While growing, cryptocurrency is still not widely accepted in India. Most businesses and consumers prefer to stick with traditional currency, limiting the practical use of digital coins.
Challenges of Traditional Currency in India
Inflation and Devaluation
Traditional currency is susceptible to inflation and devaluation, especially in times of economic crisis. This can gradually diminish the value of money.
Counterfeiting Issues
Counterfeiting remains a significant problem in India, with fake currency notes in circulation posing a threat to the economy’s integrity.
High Transaction Fees
Banking and financial services often come with high transaction fees, particularly for cross-border payments and international remittances.
Dependency on Banking Infrastructure
Traditional currency relies heavily on the banking infrastructure, which can be a limitation in remote or underbanked areas where access to banks is limited.
Government Stance on Cryptocurrency in India
The Indian government has had a cautious approach towards cryptocurrency. Initially, there was a complete ban on cryptocurrency transactions, which was later lifted by the Supreme Court in 2020. Since then, the government has been exploring the possibility of regulating the market rather than imposing an outright ban.
Recent developments indicate that India might introduce a central bank digital currency (CBDC) while regulating private cryptocurrencies. The future of cryptocurrency in India depends heavily on these regulatory decisions.
Public Perception of Cryptocurrency in India
The Indian public is gradually warming up to the idea of cryptocurrency, though there is still a lot of skepticism. Awareness about digital currencies is increasing, particularly among the younger demographic and tech-savvy individuals.
However, trust remains an issue, with many people wary of the volatility and regulatory uncertainties associated with cryptocurrency. Adoption rates are growing, but they are still far from mainstream.
The Future of Cryptocurrency in India
The future of cryptocurrency in India is promising but uncertain. If the government implements favorable regulations, there is potential for significant growth and integration of cryptocurrencies into the mainstream economy.
Challenges such as volatility, security concerns, and limited acceptance must be addressed for cryptocurrencies to thrive in India. The private sector and startups are likely to play a crucial role in driving this change.
The Future of Traditional Currency in India
Traditional currency in India is also evolving, with a push towards a cashless economy. Digital payments are on the rise, and the government’s initiatives like UPI (Unified Payments Interface) are making it easier for people to transact without cash.
While traditional currency is unlikely to disappear, its role is expected to diminish as digital alternatives become more prevalent. The global economy’s dynamics will also influence how traditional currencies function in the future.
Conclusion
In the battle between cryptocurrency and traditional currency in India, each has its strengths and weaknesses. Traditional currency offers stability, widespread acceptance, and regulatory protection, while cryptocurrency provides autonomy, lower transaction costs, and the promise of financial inclusion.
The future will likely see both forms of currency coexist, each serving different needs and preferences. As India explores this evolving financial environment, the decisions of the government, businesses, and consumers will influence the future of currency in the nation.
FAQs
- What are the main differences between cryptocurrency and traditional currency in India?
- Cryptocurrency is digital and decentralized, while traditional currency is physical and regulated by the government. Cryptocurrency operates on blockchain technology, whereas traditional currency relies on the central banking system.
- Is cryptocurrency legal in India?
- Cryptocurrency is not illegal in India, but it is not fully regulated either. The legal status of cryptocurrencies is still evolving, with the government considering various regulatory measures.
- Can cryptocurrency replace traditional currency in India?
- While cryptocurrency has the potential to complement traditional currency, it is unlikely to completely replace it in the near future.Conventional currency continues to be broadly recognized and relied upon.
- How can I invest in cryptocurrency in India?
- You can invest in cryptocurrency through exchanges like WazirX, CoinDCX, and ZebPay. It is essential to research and understand the risks before investing.
- What are the risks of using cryptocurrency in India?
- Risks include regulatory uncertainty, volatility in value, security issues, and limited acceptance. It is crucial to stay informed and take precautions when dealing with cryptocurrency.

